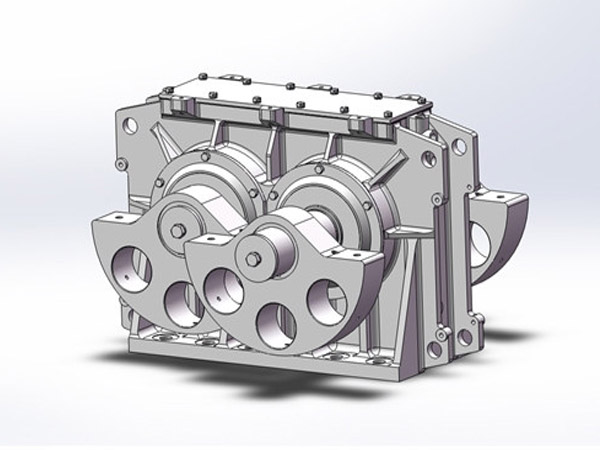
В вибрационный возбудитель является основой любой системы скрининга. Он генерирует силу вибрации, необходимую для перемещения материалов по поверхности сита., напрямую влияет на эффективность, пропускная способность, и срок службы машины. Высококачественный возбудитель обеспечивает стабильную работу., снижение затрат на техническое обслуживание, и улучшенное качество продукции.
В этом руководстве рассматриваются ключевые компоненты, соображения структурного проектирования, и стратегии оптимизации, которые помогут инженерам, руководители заводов, и покупатели принимают обоснованные решения.
Что такое виброгрохот?
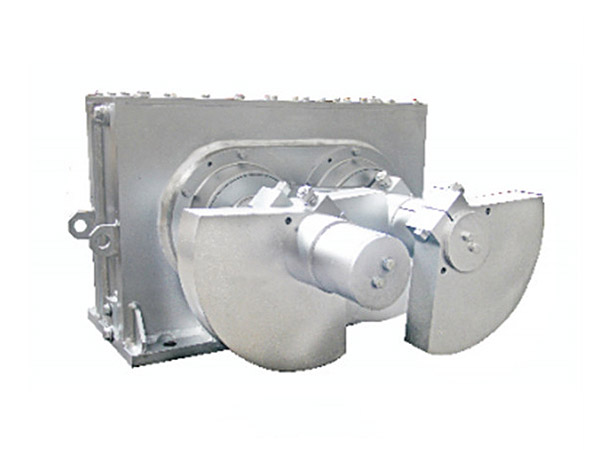
Виброгрохот-возбудитель (также называется блоком возбудителя) представляет собой механическое устройство, преобразующее энергию вращения в колебания, необходимые для эффективного просеивания материала.. Он широко используется в:
Добыча полезных ископаемых
Заполнители и строительные материалы
Подготовка угля
Металлургия
Химическая и перерабатывающая промышленность
Хорошо спроектированный возбудитель обеспечивает стабильную амплитуду вибрации., сбалансированная выходная сила, и постоянная эффективность скрининга.

Ключевые компоненты виброгрохота
Понимание основных компонентов имеет важное значение для выбора., операция, и обслуживание:
1. Корпус / Корпус возбудителя
Поддерживает подшипники, валы, и шестерни
Изготовлен из высокопрочной стали или литого сплава.
Прецизионная обработка обеспечивает стабильную вибрацию.
2. Вал(с)
Одиночный или двойной вал в зависимости от конструкции
Передаёт вращательную силу
Термически обработан, чтобы выдерживать большие циклические нагрузки.
3. горелка загружается в горячем состоянии
Сферические или цилиндрические роликоподшипники для тяжелых условий эксплуатации.
Предназначен для высокоскоростного вращения и вибрационных нагрузок.
Качество подшипников напрямую влияет на срок службы вибровозбудителя
4. Шестерни
Синхронизировать движение вала
Обеспечьте точную амплитуду и направление вибрации.
5. Система смазки
На масляной или консистентной основе в зависимости от конструкции
Предотвращает преждевременный износ и перегрев
Критически важен для долгосрочной надежности
Факторы структурного проектирования, влияющие на производительность возбудителя
Несколько конструктивных элементов влияют на производительность возбудителя.. Их оптимизация обеспечивает более высокую эффективность., меньшее время простоя, и более длительный срок службы оборудования.
…
Более подробную информацию о конструктивном исполнении виброгрохота можно найти в руководстве., пожалуйста, нажмите, чтобы посетить: https://www.hsd-industry.com/news/vibrating-screen-exciter-structure-design/