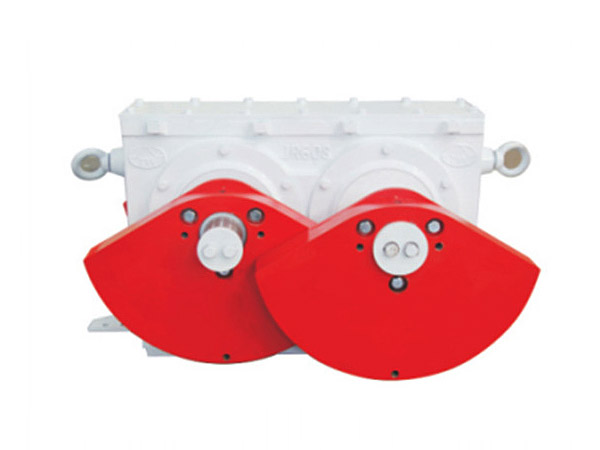
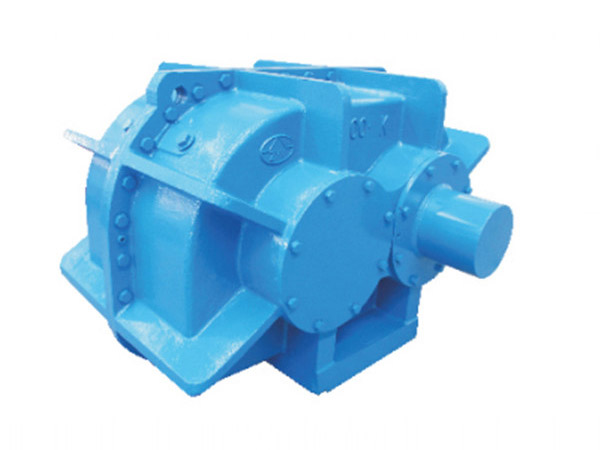
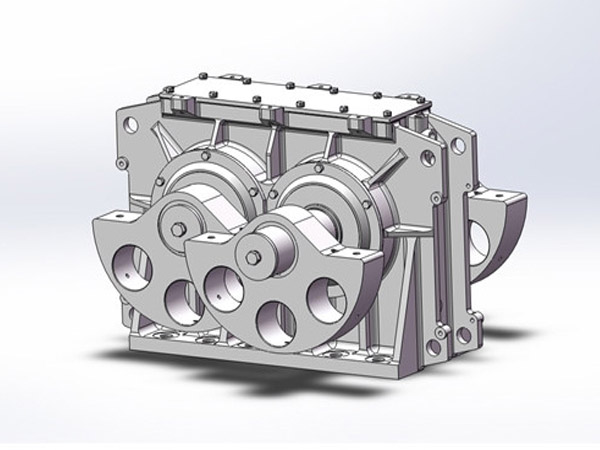
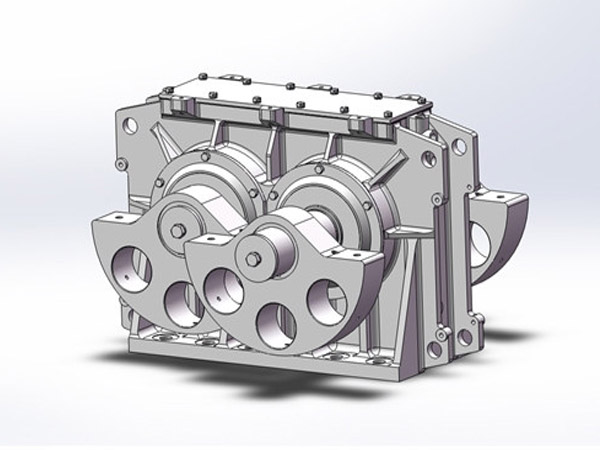
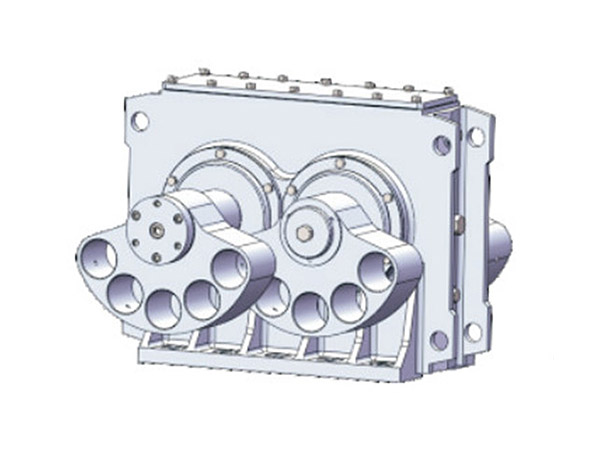
En industrias como la minería, cantera, materiales de construcción, y procesamiento químico, La detección eficiente de materiales es un paso crítico que afecta directamente la calidad del producto., capacidad de producción, y costos de operación. A medida que las especificaciones de los materiales se vuelven más exigentes, especialmente para partículas finas y ultrafinas, los métodos de detección tradicionales de baja frecuencia a menudo tienen dificultades para ofrecer resultados estables y precisos..
Aquí es donde un excitador de criba vibratoria de alta frecuencia se convierte en un componente clave para mejorar el rendimiento. Al proporcionar control, vibración de alta velocidad, mejora significativamente la precisión de la detección, reduce el tiempo de inactividad, y aumenta la eficiencia general de la planta. Causas de daños en la pista de rodadura y medidas preventivas, Exploramos las principales ventajas de utilizar un excitador de criba vibratoria de alta frecuencia en aplicaciones industriales modernas..
Beneficios de utilizar un excitador de criba vibratoria de alta frecuencia
1. Eficiencia de detección significativamente mejorada
Uno de los beneficios más notables de un excitador de criba vibratoria de alta frecuencia es su capacidad para mejorar drásticamente la eficiencia del cribado.. La rápida frecuencia de vibración crea un intenso movimiento de partículas a través de la superficie de la pantalla., permitiendo que los materiales finos pasen a través de la malla más fácilmente.
Comparado con excitadores convencionales, Las unidades de alta frecuencia son especialmente efectivas cuando se manejan:
Arena fina y concentrados minerales.
Lodos y materiales húmedos
Polvos ultrafinos utilizados en procesos químicos o industriales.
Acelerando la separación de partículas., Las plantas pueden lograr un mayor rendimiento sin sacrificar la precisión., lo que da como resultado una clasificación del producto más consistente y un mejor rendimiento posterior.
2. Mejor estratificación del material y reducción del cegamiento
La vibración de alta frecuencia promueve una estratificación efectiva del material. Las partículas más pequeñas son impulsadas hacia las aberturas de la pantalla., mientras que las partículas más grandes permanecen en la superficie y se mueven hacia la descarga.. Este proceso de separación continuo minimiza la formación de capas de material y reduce problemas comunes como el obstrucción y obstrucción de la pantalla..
…
Para obtener información más detallada sobre las ventajas de los excitadores de cribas vibratorias de alta frecuencia en el cribado industrial, por favor haga clic para visitar:https://www.hsd-industry.com/news/benefits-of-using-a-high-frequency-vibrating-screen-exciter/