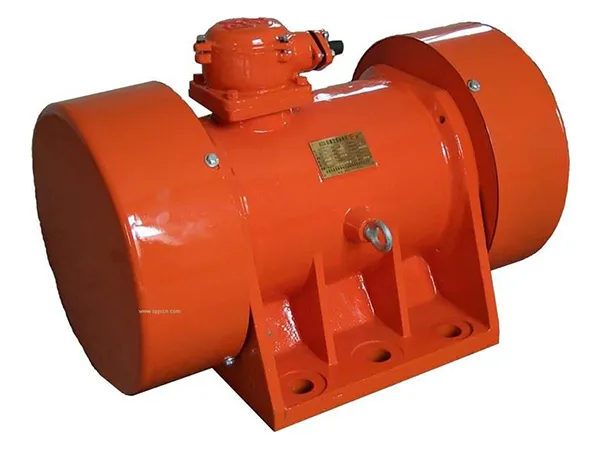
Motores de vibración are the unsung heroes of many modern technologies, providing the tactile feedback that enhances user interaction in a variety of devices. These compact, coreless DC motors are not only found in smartphones and gaming consoles but also in industrial automation, dispositivos médicos, and even wearable technology for rehabilitation purposes. As technology advances, the role of vibration motors continues to expand, offering new possibilities in how we interact with the digital world.
Technical Insights
Vibration motors operate on the principle of an unbalanced weight that spins within the motor, creating the characteristic vibration. Recent research has focused on reducing noise and vibration in more complex motor structures, such as the tangential magnetizing parallel structure hybrid excitation synchronous motor (TMPS-HESM). Studies have developed analytical models for radial electromagnetic force waves, leading to optimizations that can effectively reduce electromagnetic vibration and noise.
Vibration Motors Applications

Electrónica de consumo
In consumer electronics, vibration motors provide haptic feedback, enhancing the user experience in devices like smartphones, gaming consoles, and wearable devices. They offer a silent notification system that is both effective and power-efficient.
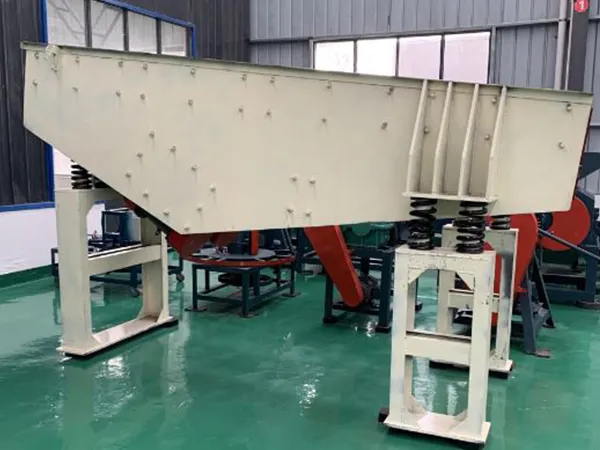
Automatización industrial
In industrial settings, vibration motors are used in applications such as vibrating screens and conveyors, compactors, and other machinery where rhythmic shaking is required for processing materials.
Dispositivos médicos
The medical field has seen innovative uses for vibration motors, particularly in rehabilitation. Wearable devices like the VTS Glove provide vibrotactile stimulation to aid in the recovery of motor function in stroke survivors.
…
For more detailed information on vibration motor applications, por favor haga clic aquí: https://www.zexciter.com/en/a/news/vibration-motors-applications.html