Fieltro de grafito es un material de aislamiento ampliamente utilizado y altamente efectivo en hornos de vacío, particularmente para aplicaciones de alta temperatura. Aquí hay un desglose de sus características, ventajas, y consideraciones.
¿Qué se siente el grafito??
El fieltro de grafito es un material fibroso hecho de fibras de carbono que han sido sometidas a procesos de grafitización de alta temperatura. Se puede fabricar a partir de varios materiales precursores como poliacrilonitrilo (CACEROLA) o Rayón. los “sintió” estructura, a menudo golpeado con aguja, le da una baja densidad y alta porosidad, que son cruciales para sus propiedades aislantes. Típicamente hay dos formas:
Fieltro de grafito suave: Flexible y se puede moldear alrededor de las paredes del horno.
Fieltro de grafito rígido (o fieltro de grafito curado): Hecho impregnando fieltro suave con resina, luego curarse y grafitarlo para crear formas autoportantes.
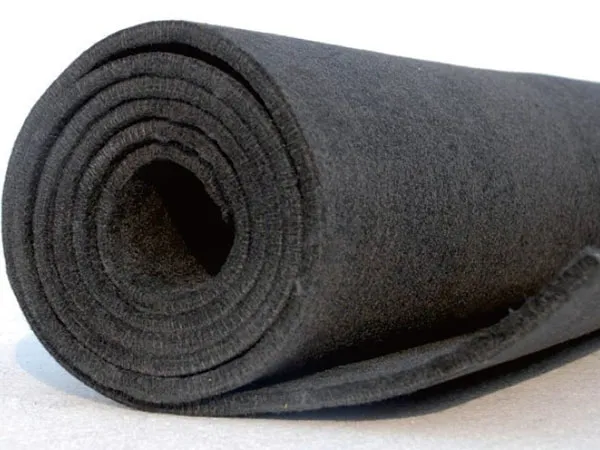

Cómo funciona como aislamiento en hornos de vacío:
El fieltro de grafito se destaca como aislamiento en hornos de vacío debido a varias propiedades clave:
Excelente aislamiento térmico: Su baja densidad y poroso, estructura fibrosa crea numerosos espacios de aire pequeños (o huecos de vacío en un horno de vacío) que impide significativamente la transferencia de calor por conducción. Esto da como resultado una conductividad térmica muy baja, especialmente a altas temperaturas. En comparación con la tabla de grafito, El fieltro de grafito tiene una conductividad térmica significativamente menor, conduciendo a menos pérdida de calor.
Estabilidad de alta temperatura: El grafito es una alotrape de carbono, y en un vacío o atmósfera inerte, puede soportar temperaturas extremadamente altas (hasta 3000 ° C o incluso más) sin fusión o degradación significativa. Incluso exhibe un aumento en la fuerza a medida que aumentan las temperaturas.
Baja masa térmica: Su naturaleza liviana significa que absorbe menos calor, Permitir que el horno alcance las temperaturas de funcionamiento más rápido y se enfríe más rápidamente, contribuyendo a la eficiencia energética y los tiempos de ciclo más cortos.
Buena resistencia a la choque térmico: El fieltro de grafito puede soportar cambios rápidos de temperatura sin grietas ni deformarse, Mantener su integridad estructural en entornos de horno exigentes.
Inercia química: En atmósferas no oxidantes (vacío o gas inerte), El grafito es altamente resistente a muchos productos químicos y medios corrosivos, que es crucial para prevenir la contaminación de los materiales procesados.
Facilidad de mantenimiento e instalación: El fieltro de grafito suave es relativamente fácil de cortar, forma, y reemplazar, Hacer que las reparaciones y modificaciones sean más simples en comparación con los materiales rígidos de la placa. También se puede maniobrar alrededor de los puntos de montaje y las boquillas..
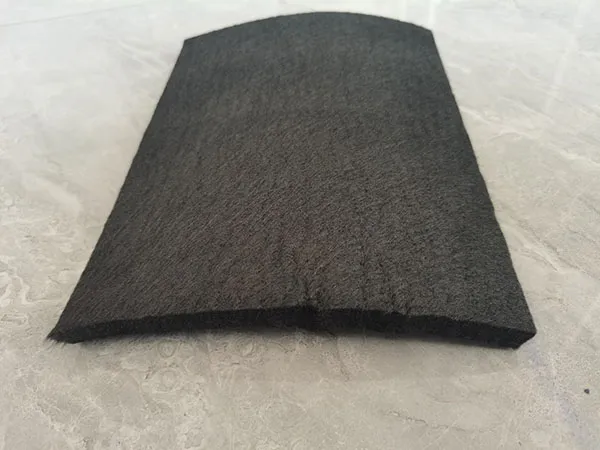

Ventajas del aislamiento de grafito de fieltro:
Eficiencia energética: La baja conductividad térmica minimiza la pérdida de calor, Reducción del consumo de energía y costos operativos.
Tiempos de ciclo más rápidos: La masa térmica baja permite un calentamiento y enfriamiento más rápido, Mejora de la productividad.
…
Para obtener más detalles sobre cómo se desempeña grafito como aislamiento en hornos de vacío, por favor haga clic aquí:https://www.czgraphite.com/a/news/graphite-felt-for-vacuum-furnace-insulation.html