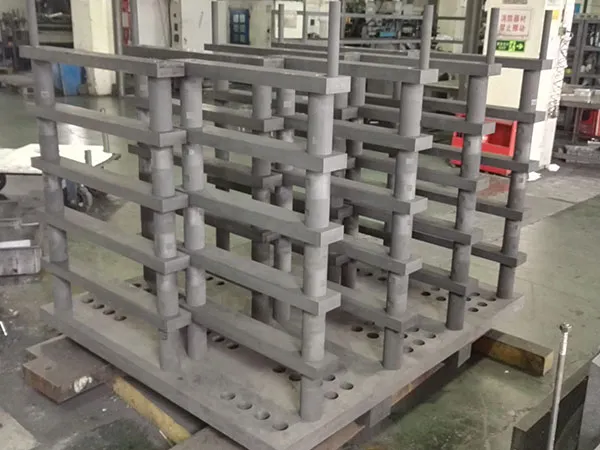
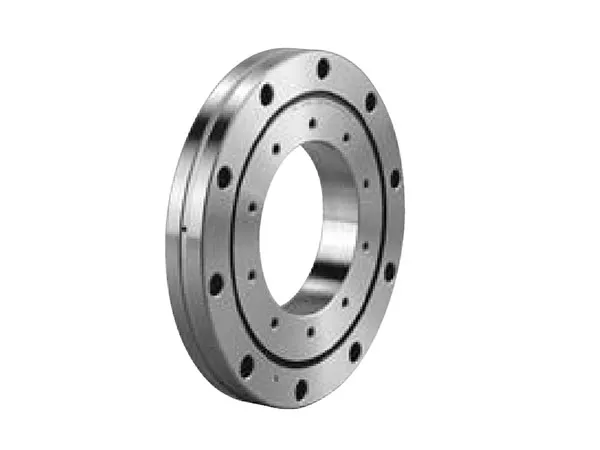
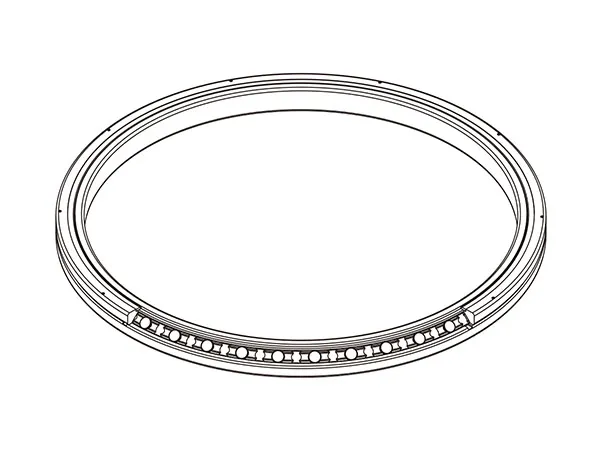
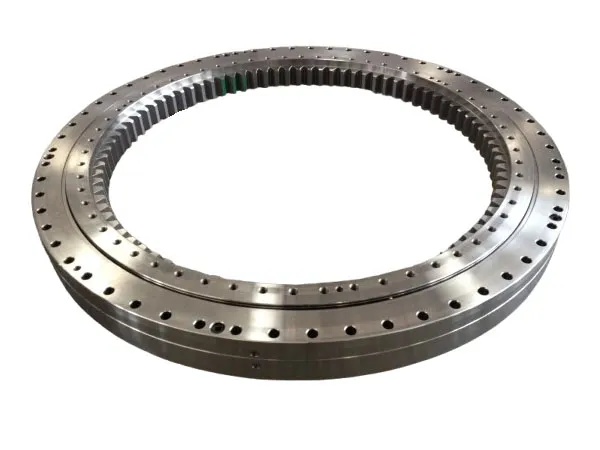
Personalizar un estante de grafito para un horno de vacío es un proceso crítico para optimizar el rendimiento, Asegurar la calidad de la parte, y maximizar la vida útil de los componentes de su horno. A well-designed custom rack can make a significant difference in your operations.Customizing a estante de grafito de horno de vacío involves a collaborative process with a manufacturer to design and fabricate a rack that meets your specific application needs.
Why Customize? The Benefits
Maximize Load Capacity: Fit more parts in each cycle, increasing throughput.
Improve Part Quality: Ensure uniform heating and gas flow around each part, reducing warpage and ensuring consistent metallurgical properties.
Prevent Contamination: Hold parts securely without direct contact where it’s not desired, and use the right material grade to prevent reactions.
Enhance Ergonomics: Design for easy loading and unloading, reducing operator strain and cycle time.
Increase Rack Lifespan: Use the appropriate material and structural design to withstand thermal cycles and mechanical stress.
Vacuum Furnace Graphite Rack Customization Process
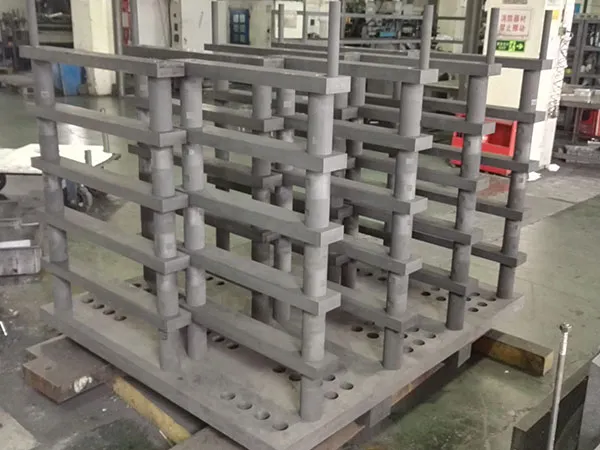

The process typically follows these steps:
Step1: Defina sus requisitos
Evaluación de necesidades: You provide the manufacturer with the specifics of your application. Esto incluye:
Part Geometry and Size: The dimensions and shape of the parts you will be placing in the rack.
Loading and Weight: The total weight of the parts the rack needs to support.
Temperatura de funcionamiento: The maximum temperature the rack will be subjected to inside the furnace.
Required Durability: How long you expect the rack to last and how many thermal cycles it needs to endure.
…
For more detailed information on how to customize vacuum furnace graphite rack, por favor haga clic aquí:https://www.czgraphite.com/a/news/customized-graphite-rack-for-vacuum-furnaces.html