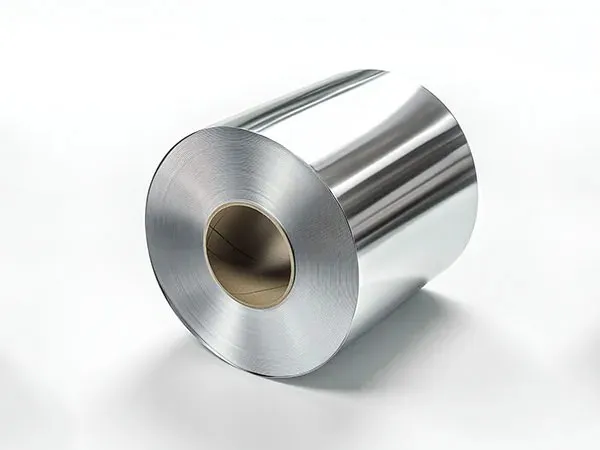
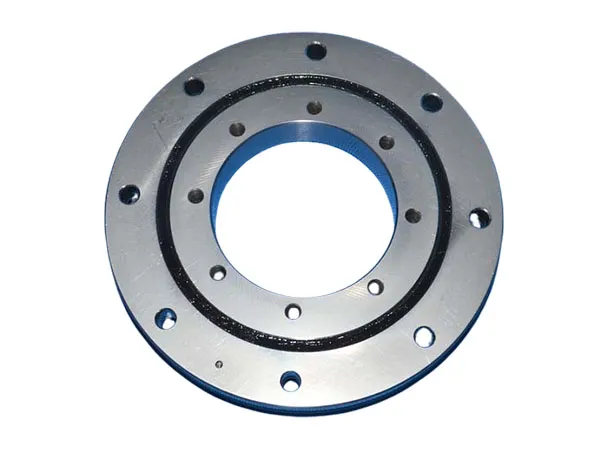
Bobinas de aluminio son esenciales en la industria moderna, construcción, y proyectos arquitectonicos, ofreciendo peso ligero, durable, y soluciones resistentes a la corrosión. Elegir el acabado correcto de la bobina de aluminio (bobinas de aluminio prepintadas o bobinas de aluminio anodizado) puede influir significativamente tanto en el rendimiento como en la apariencia.. Comprender sus beneficios, aplicaciones, y las diferencias ayudan a los fabricantes, diseñadores, y los ingenieros toman decisiones materiales informadas.
Bobinas de aluminio prepintadas: Elegante, Protector, y personalizable
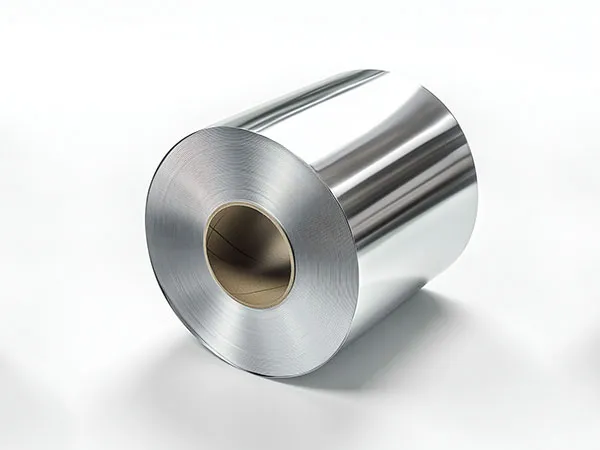

Bobinas de aluminio prepintadas, también conocido como PVDF o aluminio recubierto de bobina, están recubiertos con una capa de pintura protectora durante la producción. Este revestimiento mejora la estética con colores vivos., texturas, y acabados, al mismo tiempo que mejora la resistencia a la corrosión y la durabilidad a la intemperie..
Beneficios clave:
Apariencia personalizable: Amplia gama de colores, texturas, y acabados para paneles arquitectónicos y aplicaciones industriales.
Protección duradera: Resistente a los rayos UV, humedad, y contaminantes ambientales
Bajo mantenimiento: Las superficies lisas son fáciles de limpiar y mantener.
Aplicaciones típicas:
Fachadas de edificios, paneles para techos, y revestimiento
Señalización, tableros publicitarios, y elementos decorativos
Diseños arquitectónicos interiores y exteriores.
Bobinas de aluminio anodizado: Durable, Resistente a los arañazos, y ecológico
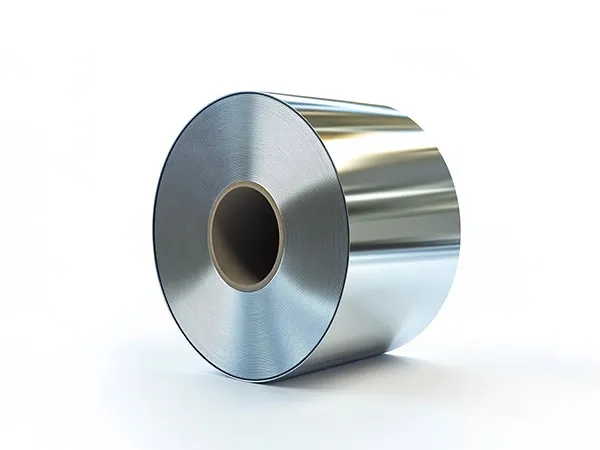

Las bobinas de aluminio anodizado se someten a un proceso electroquímico que espesa la capa de óxido natural, produciendo un duro, superficie resistente a la corrosión. a diferencia de la pintura, El anodizado penetra en el propio aluminio., ofreciendo durabilidad y longevidad sin volumen añadido.
…
Para obtener información más detallada sobre las diferencias entre las bobinas de aluminio prerrevestidas y las bobinas de aluminio anodizado, por favor haga clic para visitar:https://www.dw-al.com/a/news/pre-painted-vs-anodized-aluminum-coils.html